The concept of calculating frequency from wavelength is fundamental in the study of waves, including electromagnetic waves like light and radio. Understanding how these two properties relate, and how to calculate frequency from wavelength, can be useful in fields like telecommunications, physics, and engineering. Whether you’re working with sound waves, microwaves, or visible light, being able to make this calculation helps you describe the wave’s behavior and determine how often it oscillates in a given time frame.
Below we offer a wavelength to frequency calculator to help you make this useful determination. We also offer a handy wavelength calculator (linked above) on the Pasternack website.
What are Frequency and Wavelength?
Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive peaks or troughs in a wave. It’s typically measured in meters (m) but can also be expressed in smaller units like nanometers (nm) when discussing light waves or micrometers (µm) for infrared waves.
Frequency, on the other hand, refers to how often a wave passes a particular point in a given time period. It’s usually measured in hertz (Hz), where 1 Hz equals one cycle per second. For example, if a wave passes a point 500 times per second, its frequency is 500 Hz.
Relationship Between Frequency and Wavelength
The key equation that links frequency (f) and wavelength (λ) is:
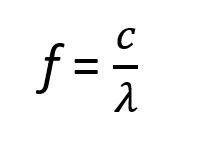
Here:
- f is the frequency,
- c is the speed of the wave (for electromagnetic waves in a vacuum, it’s the speed of light, approximately 3 × 108 m/s,
- λ is the wavelength.
In simple terms, the frequency of a wave is equal to the speed of the wave divided by its wavelength. The speed of light (c) is a constant when dealing with light in a vacuum, but for other types of waves, like sound waves, the speed of the wave depends on the medium (air, water, etc.) through which it travels.
Example Calculation
Let’s say we are given a wavelength of 600 nm (nanometers), which is a typical wavelength for red light. Since we need to calculate frequency, we first need to convert the wavelength from nanometers to meters because the speed of light is in meters per second.
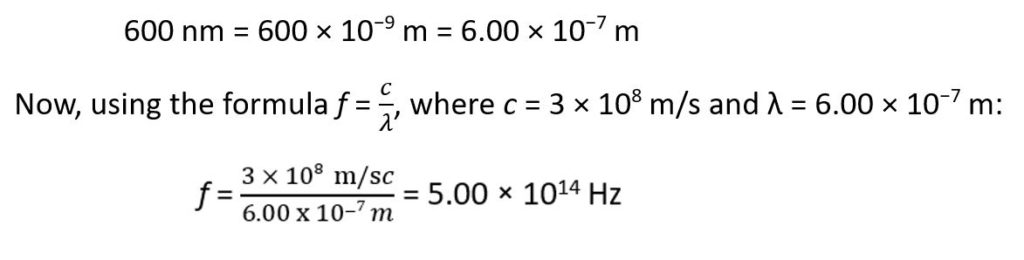
Thus, the frequency of light with a wavelength of 600 nm is 5.00 × 1014 Hz.
Why This Matters
Understanding how to calculate frequency from wavelength is crucial in fields such as telecommunications, astronomy, and physics. In telecommunications, different frequencies are used to transmit signals like radio, television, and internet data. Knowing the wavelength of a signal allows engineers to determine the frequency and optimize the performance of communication systems.
In astronomy, scientists use the relationship between frequency and wavelength to analyze light from distant stars and galaxies. By measuring the wavelength of the light, they can calculate its frequency and infer critical information, such as the star’s temperature and the chemical elements present in it.
Summary
Calculating frequency from wavelength is a straightforward process once you know the wave’s speed and wavelength. The fundamental relationship f = provides a simple yet powerful tool to understand and describe wave behavior. Whether you’re dealing with visible light, radio waves, or sound waves, knowing how to calculate frequency from wavelength with this frequency and wavelength formula is essential in many scientific and technological applications.




 Pasternack Blog
Pasternack Blog
